Home → Users Manual → Printer Friendly Version
Users Manual
- 1. Welcome
- 2. The Workspace
- 3. Workspace: Left Navigation
- 4. Workspace: Request Grid
- 5. Workspace: Top Navigation
- 6. Filters
- 7. The Request Page
- 8. Responses
- 9. HelpSpot AI
- 10. Knowledge Books
- 11. Reports
- 12. Customer Portal
- Appendix: Feature In-Depths
1. Welcome
1.1. The Big Picture
If you're reading this manual you've realized that email folders, sticky notes, or even your current help desk tool are no longer the way to handle Customer inquiries. You're looking for an improved experience for Staff and Customers with more advanced capabilities to manage your support operation...Welcome to HelpSpot!
HelpSpot's core function can be summed up as:
"HelpSpot is a web-based application that empowers companies to effectively manage Customer inquiries."
To create a product that is optimized to support this core function, we kept a few guiding principles top-of-mind:
Accommodate many support channels
Customer inquiries come at you from every direction. HelpSpot accounts for this by supporting the channels you need:
- Email (your current support email account) HelpSpot is optimized for email-based exchanges,
- Web-form (using the portal),
- Phone/walk-up/fax/IM (via User creation), and
- API (covered in API Manual, linked)
Create structured flexibility
The needs of every company differ; some require elaborate issue categorization and meta-data collection capability, while others only loosely categorize issues. To accommodate all types of companies, we provide a structured framework of data collection/categorization that is fully customizable yet still easy to report against.
Require request ownership
Individual ownership is required in HelpSpot. Requests cannot be assigned to a nebulous workgroup or department. Individual ownership is the cornerstone of driving processing efficiency and ultimately Customer satisfaction.
Create a clear, concise, request history
Every request has a complete log of all actions taken and messages sent. This allows any User, at anytime, to become current with a request.
1.2. Targeted Audience and Common Terms
Targeted Audience
This manual is intended for all HelpSpot Users, those new to help desk software as well as those migrating from another product.
Administrator-specific settings and configuration options are not covered in-depth in this manual.
Common Terms
The following terms are used throughout this guide:
- User Anyone with a HelpSpot account.
- Staff Generically refers to any help desk staff member.
- Staff level User with Help Desk Staff level permission to HelpSpot.
- Administrator User with Administrator level of access to HelpSpot.
- Editors Users with capability to create knowledge book content.
- Moderators Users with ability to manage interactions in forums.
- Customer Refers to a support desk's Customers (internal or external): the individuals submitting requests.
- Request The Customer inquiry in HelpSpot.
- Installation The instance of HelpSpot used by a company.
1.3. Default Levels and Permissions Groups
A Users permissions settings and/or level dictates access to features. Permissions are set by Administrators, typically at time of Staff account creation. Staff can be assigned one permission group. The permission group is not related to any individual request or set of requests. Instead, permission groups control access to various actions and areas inside of HelpSpot.
Default Permission Groups
When HelpSpot is initially setup a default set of permission groups are created. In addition there is always an Administrator permission group. The Administrator permission group is a super user level that allows unlimited access to the system. The Administrator group cannot be removed or modified.
Modifying Permission Group
The permissions settings for any of the default permission groups can be modified, through the permissions group management area in the Administration section of the site (accessible by Administrator level only).
Creating New User Levels (Permission Groups)
Administrators can use the Permission Groups area to create a new permissions group. New Groups can be cloned from existing User levels for ease of creation.
1.4. Getting Up and Running-Administrators
While this guide doesn't specifically cover Administrator configuration, the following provides Administrators with a quick look at the most important steps for getting the installation up and running. More detailed Information on configuration can be found in the HelpSpot Administrator Manual.
- Configure System Settings Page
(Location: Admin>Settings) The settings page includes several system-wide configuration options that range from creating status types to defining the layout of the Customer portal. Administrators should review and become familiar with each as an initial step in the set-up process.
Status types are most useful for defining the resolution for each request.
- Create Support Staff Accounts
(Location: Admin>Staff) User accounts must be created and assigned access to the system. The following provides a high-level look at each permission level.
- Create Request Categories
(Location: Admin>Categories) To effectively route requests and allow for concise request reporting, Administrators will need to define request categories. Permissions for default ownership, accessibility by assigned Staff, and visibility on Customer portal must also be set for each category created. Reporting tags for each category are an optional way that further classifies individual requests.
- Create Support Mailboxes
(Location: Admin>Email Mailboxes) HelpSpot mailboxes serve as a way to seamlessly integrate email exchanges. By adding individual mailboxes, HelpSpot can pull all messages sent to existing support email account and create new requests or append notes to existing requests. Through additional configuration, Administrators can opt to route requests resulting from emails into specific categories or auto-assign to selected Staff.
- Define Custom Request Fields
(Location: Admin>Custom Fields) Custom fields are a means to create User-defined fields for the collection of meta data. With 11 different types available Administrators have a robust, structured framework for collecting the information specific to their product/service or organization.
1.5. Logging in
When an account is created, the User receives via email his/her account login information. Upon login Users are brought to the workspace which is where our guide begins.
2. The Workspace
2.1. Getting the Lay of the Land
The workspace, or the initial landing page, can be thought of as the hub of all request management within HelpSpot. It is from here that Users can access individual request management functions: creating, viewing, and updating. This chapter looks at the basic structure, layout, and function of each of the areas within the workspace.
For the purposes of understanding the overall structure, let's break the workspace out into three areas. These areas are briefly introduced below and covered in-depth in subsequent chapters.
- Left Navigation. This area includes all of the links running along the left side of the screen. These links provide access to varying request views and related actions.
- Request Grid. Conceptually, the request grid is the display area for requests meeting specified criteria. Criteria will vary depending on the filtered view the User is in. The criteria used to determine the requests displayed in the request grid (for any given filtered view) are defined by:
- Users or Administrators; through filter creation,
- System default views: the Inbox and My Queue.
- Top Navigation. This encompasses both the very top navigation items as well as those just below the navigation bar.
3. Workspace: Left Navigation
3.1. Inbox & My Queue
Inbox
On a very broad level the Inbox is home to all unassigned requests. As such, its primary function is to serve as the entry point for new requests (submitted via email, portal or other channel).
Users can take a request from the Inbox by simply clicking on the Take It button to the far left within the request grid. Upon doing so, Users will immediately be taken to the request page for that request. Ownership begins as soon as a User takes a request out of the Inbox; it is no longer shown in the Inbox and will instead show in that User's My Queue.
My Queue
As mentioned in the previous section, once a request is assigned to a User it is no longer available through the Inbox and can be found in the User's My Queue.
Request assignment can occur in several ways: User takes a request from Inbox, one User assigns a request to another User, or an automated process handles the request.
Once a User clicks My Queue, the request grid in the center of the screen will load all the open requests assigned to that User.
The list of requests shown here will vary between Users because it reflects the requests assigned to the person logged-in. Additional views, or filters, can be created and saved for viewing requests assigned to others.
HelpSpot uses My Queue as the default view when Users login and click the Workspace tab. However, this is customizable, allowing Users to select any filtered view as the default.
3.2. SPAM & Trash
SPAM (overt advertising, typically created via an automated process) is a common problem for support centers that openly publish support email addresses or web-forms. To prevent it from interfering with true Customer inquiries or incorrectly skewing reporting, HelpSpot has integrated a trainable SPAM tool.
Training the SPAM Tool
HelpSpot will initially depend on Users to flag requests that are SPAM. Over time, while this flagging is being done, HelpSpot will learn to recognize the SPAM specific to the installation and automatically flag it accordingly.
Users can flag requests as SPAM in either the request grid (using the quick action buttons) or in the request itself.
All requests flagged as SPAM are available via the SPAM link in the left navigation. From here, Users can use the request grid to click into the request or select and delete it.
Messages which are sent to SPAM but later marked as NOT SPAM by a User also helps train the SPAM tool to not incorrectly mark requests as SPAM.
Removing Flag or Deleting SPAM
If either a User or the SPAM tool incorrectly flags a request as SPAM, check the box next to the request and use the drop-down at the bottom of the request grid to select Mark as Not SPAM. After hitting submit the request will move into the Inbox where it can be taken by any User. Marking a request as NOT SPAM will train the SPAM tool to not mark notes from that sender as SPAM.
SPAM must be deleted to reinforce the systems learning process. To delete, check the box next to each request and use button at the bottom of the request grid to delete the SPAM. Once this is done it will be completely removed from HelpSpot.
Trash
Requests that aren't necessarily SPAM but don't need to be worked or counted towards reporting can be flagged for the Trash. Using the Trash is a means for handling email bounces, training/test requests, and duplicate requests.
3.3. Search
HelpSpot provides users with a several different ways to find requests within the system.
Quick Search
Quick search is located in the left hand navigation bar. If a request id is entered, the user will be taken directly to that request. Otherwise, a full text search is performed. Full text search modifiers can be used in this box.
Advanced Search
Advanced searches can be done on a myriad of customer, request, and installation-level details. You can access the advanced search tool in the top menu bar.
Customer Searches
Users can search against any/all customer specific information found on the request page. Results are returned below the search boxes and clicking the linked request ID will allow Users to go directly to the request page for the individual request.
Detailed Searches
This search type allows Users to create a more intricate, specific set of search criteria. At a high level, the parameters by which Users can search are grouped by the following:
- customer information
- request details
- custom fields
- request history
- date & time (minutes/hours since or before specified actions)
- assignment chain (who/when of request ownership)
- public updates (by whom and number of)
- any/all conditions and custom SQL
Turning Searches into Filters
Users need to go into the filtered view to modify filter (such as making Global or modifying columns). Once in the filtered view, select the edit filter link in the options menu to make the necessary changes. For more on managing filters, see the filters page.
Full Text Search
Full text searches allow users to search either the knowledge books for request history with full text queries. Advanced syntax can be used to narrow or broaden your search.
Syntax
- Use + for must contain: +printer, +password
- Use - for must not contain: -printer, -password
- Use " " for a phrase: "lost my password"
- Use * as a wildcard: print*
Examples
Search must contain "password" and "reset" but not contain "windows":
+password +reset -windows
Search must contain the phrase "Budget Report" and the word December:
+"Budget Report" +December
Search can contain either Password or Login
Password Login
3.4. Viewing Filters
Filters are custom-created views of requests. Each filter has a set of criteria, defined by the creator using specific conditions that requests must meet to be returned in the results set. Filtered views can be created and saved on the User or global level.
At the bottom of the left nav, Users will see a list of both personal and global filters. Personal folders can be listed individually on the left nav or grouped into folders. To access the contents of a filter, click the filter name.
Modifying Filter Views
To modify the properties of a filtered view, simply click the edit link in request grid view.
For more on the specifics of Filter modification, see the Filters page of the manual.
4. Workspace: Request Grid
4.1. General Layout
The request grid is the display area for requests meeting specified criteria. The criteria will vary depending on the filtered view (Inbox, My Queue, or custom-filtered view) the user is in.
At the top of every request grid is the name of the view. For those views that are system created, it will be the names designated by HelpSpot; Inbox and My Queue. For those views created by Administrators or Users, via filters, it will be the name designated during filter creation. Just after the view name, Users will find a request count. This count reflects the number of requests that match the defined conditions.
To the far right of the name and count the filter menu allows access to other filter functions.
- Edit. If the current user is the filter owner or an admin they can edit the filter criteria.
- Stream: Users can go between the request grid and the note stream layouts. These views are described more in-depth below.
- Options: Within the options menu, Users have access to delete filter or make the filtered view the default workspace. Every filtered view can be exported into a .csv file or viewed via an RSS reader.
Request Grid: Default Columns
The request grid returns specific information, in columns, for each request that is included in the results set for the view. The Inbox and My Queue have a default set of columns that are returned. Those columns returned in custom-created filtered views are defined by upon creation. Working left to right in the request grid, the default columns are outlined below.
- Quick Action check box. The check box to the far right of all requests is used to select the request(s) for which one of the quick actions will be taken. A complete list of quick actions available is discussed later in this chapter.
- Take It (Inbox or custom filtered view only). Allows Users to take a request to work. Once clicked, Users will be brought to the request page. At this point the request is assigned and will no longer be visible in the Inbox.
- Read/Reply Indicator. A graphical indicator of the most recent action taken on the request.
|
Green dot. The most recent update to the request that is unread by the assigned User. |
|
|
Grey dot. User has read the update but a Staff member has yet to reply. |
|
|
Circular Arrow. Staff member was the last to reply. |
Users can click the green/grey dot to change the read/unread state.
- Request ID. This is the ID auto-assigned to each request when it enters the system. Within the Inbox, there is no request ID but rather the Take It button.
- Customer Name. First and last are shown, if provided.
- Initial Request. Shows the first few sentences of the initial request sent by the Customer. The text can be clicked to preview the body of the message.
- Age. Shows the length of time that has passed since the initial request was created.
Note Stream View
By default, HelpSpot loads each filtered view a grid-type layout (as outlined above). However, on the fly, Users can switch to the note stream view that shows only the real-time activity of requests. Users can specify if they want to see the following update types:
- Staff only (public updates)
- Staff only w/private
- Customer only
- Customer & Staff
Users can think of this view as a timeline of request activity within the filtered view.
Simply clicking the grid-like icon will return Users to the standard, request grid view.
4.2. Quick Actions Buttons
The quick action buttons allow users to perform actions on request(s) directly from the request grid page, saving the need to enter the request page for each individual request. Quick action buttons can be found at the bottom of the request grid in all filtered views.
All actions are performed by selecting the checkbox next to the desired request(s), then click the desired action button.
Available quick actions include:
- Reassign. Users can opt to assign a new category and Staffer to the selected requests. When used in conjunction with category auto-assignment (if enabled), it can serve as a means to manage workflow based on issue types.
- Close. When a group of requests does not require further action they can be closed directly from the request grid. Prior to action being completed, Users must select the appropriate closing status types.
- Batch Respond. This action allows Users, in one step, to update multiple requests.
- Merge. Allows for the request history of one, or more requests, to be forced into another.
- Status. Users can quickly change the status for a group of requests.
- Trash. A means to remove testing/training requests, duplicate requests, or any other requests that do not require action or should be removed from the system for reporting purposes.
- SPAM. Will flag all selected requests as SPAM and move to the SPAM filtered view for deletion.
4.3. Display Options and Editing
At the top of each filtered view, within the name header, Users will find various options for viewing/editing that view.
Request Grid View and Note Stream View
The details of these view are described more in-depth on the General Layout page, linked under related pages.
Options
For each filtered view, Users have a few options available to them. The Inbox and My Queue, because they are system default views, have a limited list of options available.
Customize Columns
Only available for Inbox and My Queue. Allows Users to configure those default items included in the request grid view.
Edit Filter
This only shows to the filtered view creator or an Administrator. From this link, the parameters of filtered views, permissions, and how they are displayed can be modified.
Make Default Workspace
Any filtered view can be made as a Users default landing page when entering the Workspace. When used in conjunction with a Take It button, any filtered view can be used as an organizations/work groups default inbox.
RSS and .CSV export. The contents of any filtered view can be exported to either an RSS reader or .csv supporting application.
5. Workspace: Top Navigation
5.1. Accessing Other Areas
Along the top, Users will find icons to access other areas of HelpSpot. Not all icons are available for all User levels.
Top navigation icons include:
| Workspace | The initial landing page, can be thought of as the hub of all request management within HelpSpot. |
| Knowledge | Allows an organization to create documentation for their products/services. |
| Reports | A comprehensive, customizable and graphical way to monitor the activity on your help desk. |
| Responses | Allows for the creation of response macros that can be used in requests in addition to scheduled requests. |
| Admin | The administrative area where HelpSpot is configured and business rules are created. |
| Access the advanced search tool | |
| Access customer facing portals | |
| Access personal staff settings and configuration options. |
5.2. Create a Request
The create request button, below the top navigation, is used to manually create requests. Requests would typically enter the system via email, portal form, or API. However, there is a means to create request for such customer encounters such as phone or IM.
Once a User clicks the create request button, the request page loads.
5.3. Subscriptions & Reminders Lists
Subscriptions
Users can follow changes made to requests that aren't assigned to them by opting to subscribe to a request. In any request that a user is not currently assigned, they can use the star icon next to the request id to subscribe to notifications on future updates.
As the assigned user of a request you can also subscribe another user to the request using the option in the staff notification area of the request.
Reminders
From the request page of an individual request, Users can set a reminder. Reminders are emailed at the designated date/time to selected Users and are listed under the reminders area of the workspace.
Managing Subscriptions and Reminders
Both subscriptions as reminders can be accessed for a given user by clicking on the user menu. Subscription and reminders can be removed from this screen.
6. Filters
6.1. Filters Overview
Filters are custom-created views of requests. Each filter has a set of criteria, defined by the creator using specific conditions that requests must meet to be returned in the results set. Filtered views can be created for use by various groups of Users. The filters button can be found just below the top navigation, above the request grid, in the Workspace.
Defining Conditions
When creating a filter, Users can define an infinite number of conditions, and combination of conditions, that requests must meet to be included within that view. Conditions are based on individual elements of the request, Customer, or actions taken on a request. Users must define if the requests should match any or all conditions provided for the filter.
For each condition there is a means to define the value, via either a drop-down or text field. Each condition provides an additional drop-down for selecting the operator (for example: greater than, less than, is/is not) to define how the specified value is applied.
For more advanced filter creation, sub- or nested groups of conditions can be created using the advanced condition of ALL/ANY of the following are true. When either is used, nested drop-downs will appear where the sub-condition group is created.
Filter Conditions
Customer Information
- Customer ID
- First name
- Last Name
- Phone Number
Request Details
- Request ID
- Assigned to
- Category
- Status
- Open/Closed
- Is Urgent
- Is Not Urgent
- Reporting Tags
- Opened By
- Email Subject
- Contact via
- Mailbox
- Portal
Custom Fields
- Checkbox
- Dropdown
- Drill Down
- Date & Date/Time - Less than, greater than, various time periods (past 30/60/90 days), etc.
- Text Boxes
- Etc.
Search
- Request history full-text search for _____
Date and Time
- Relative Date Since Opened
- Relative Date Since Closed
- Minutes since opened
- Minutes since closed
- Minutes since last update
- Minutes since last public update
- Minuets since last customer update
- Minutes since first response (all hours)
- Request Updated
- Request Publicly Updated
- Customer Updated Request
- Opened Before Date
- Opened After Date
- Closed Before Date
- Closed After Date
Assignment Chain
- Reassigned from/to
- Was ever assigned to
- Reassigned by - includes all users plus settings for the system and whichever user is logged in
Other
- Number of public updates
- Last public reply from
- Updated by (use with other conditions)
Advanced
- ALL of the following are true - allows you to create nested conditions
- ANY of the following are true - allows you to create nested conditions
- Customer “where” clause (SQL)
Integrations
- Thermostat NPS Score
- Thermostat CSAT Score
- Has Thermostat Feedback
Testing Conditions
To test the condition(s), Users can hit the Run filter button just below the conditions box. The results will truncate to show only the first 30 requests in the results set. However, the top of the results set shows the number of requests that match the condition(s) set. To see all requests, check the Show all Results box prior to running.
The results will return based on the preferences set in the Save filter box to the right of the screen. To see the results set, with the desired preferences (such as columns and sort) included, set preferences before running the test.
Once a User is satisfied with the conditions set, as demonstrated through the results presented in the testing, they can move to the final steps of setting preferences and saving.
Options
Viewing
As mentioned in a previous chapter, all filtered views are displayed and accessed via the left navigation (nested or individually listed).
Editing
Administrators and the designated creator can edit a filtered view. The link to edit can be found under the options link within the request grid layout of the filtered view. Once clicked, Users will be brought to the filter creation/modification page.
6.2. CSV Export
Filters can be exported as CSV files for processing in spreadsheet, graphing and data analysis applications. To export a filter as a CSV file, first setup the filter with the desired criteria and columns. Then, after your filter is saved, select the options menu and then select "CSV Export."
7. The Request Page
7.1. Concept and Contents
The request page is the Customer email, portal form submission, or phoned-in inquiry translated into a request; it's the core of individual inquiry/request management. From here, Staff can reply to the Customer, add meta-data, categorize, and assign the request.
The request page is accessible only for those with a HelpSpot account. The primary ways Users will access the request page include:
- Clicking the Take It button from the Inbox
- Clicking the request ID from the request grid of any view
- Clicking Create a Request in the left navigation of the workspace
- From a link in an Update email
Navigating Requests within a Filtered View
When a filtered view (including inbox and workspace) has more than one request, Users can easily navigate between requests through the use of the next and previous buttons in the top right of the request page. This eliminates the need to go back to the workspace to enter the next request.
Request Page Layout
For the purposes of understanding functionality, the request page can be divided into 5 main areas.
- Customer Details
- Time Tracker (if enabled)
- Request Note
- Request History
- Request Details
7.2. Customer Details
For every request, HelpSpot provides fields for logging Customer-specific information.
HelpSpot will automatically populate as much information as possible for requests initiated via the portal form or an email. For requests manually entered by Staff, the Staff member must enter the Customer information as part of the request creation process.
History Search
Within the History Search tab, Users can see all open requests for that customer. Searches default to General, however it can be quickly adjust to search on such parameters as domain name or Customer ID. Upon clicking the Customer ID for any request, you see a preview of the request with the option to insert customer data in the current request.
Live Look Up
Live lookup allows HelpSpot to communicate with an external database (or other system that stores Customer data, pertinent to the support staff desk). Its power is it provides real-time display of data from external systems within HelpSpot, ensuring Customer information and custom field data is always accurate. For information on configuring Live Look Up, see the Administrators Manual.
7.3. Creating a Note: Formatting and Note Types
HelpSpot offers two formats for creating/sending updates via email: HTML (via visual editor or formatted text) or plain text.
HTML Formatting
HTML formatting can be done in one of two ways, via a visual editor or formatted text. Both provide the same end-result yet require Users to apply style in different ways.
Visual Editor (WYSIWYG)
HelpSpot defaults to sending/receiving HTML emails; so 'out of the box' Users will see a formatting tool bar across the top of the note box to support the sending of HTML emails. This tool bar functions similar to formatting tool bars in Microsoft Word. To format text, type in the box, highlight and click the desired formatting option.
Formatted Text
For installations with formatted text enabled, HelpSpot uses a formatting text mark-up to modify how text is displayed. Formatting covers the basics most Users would need for a note such as bolding, underlining, linking, and bulleted lists. HelpSpot converts the mark-up into HTML once the User submits the update. The Formatting Options link opens a window listing the characters that must be used to achieve the various formatting effects and serves as a reference when applying styles.
Note Types
As we review the note types, keep these key HelpSpot principles in mind:
- Customers receive email notices only when a public note is used.
- All note types are logged within the request history.
- The assigned Staff person receives an email when other Staff person updates the request.
- HelpSpot appends the request ID to every outgoing message for the logging replies in the request history.
Public Notes
These notes are used to provide the Customer an update on their inquiry. Public notes are:
- available to Customers via the portal, and
- are emailed to the Customer (via the email in the Customer information box).
Add Notifications and Modify Sending Settings
Notifications and sending settings are configured in the Email Options area. Click on the Email Options area to view these options.
Staff can be added to notifications through this menu or they can be tagged using the "@" hotkey in the request note editor.
Others, outside of the Customer or Users, can also receive a public note. Those individuals should be listed as a CC or BCC.
To add a recipient, click the Add a CC Email or Add a BCC Email, type the recipients email address and click Add.
When an email address is added, the recipient will continue to be included on all public updates until the address is removed. To remove the email address, simply click on the email icon next to the address.
As part of the public note options there are fields to modify the email subject and change the sent from email address. Users may find modifying the subject is an easy way for recipients that aren't familiar with the issue to understand the contents of the message they received.
Modifying the email subject doesn't mean you lose the interaction in HelpSpot. Because HelpSpot auto-appends the request ID to all subjects of outgoing emails, any responses will be correctly logged within the request history.
Private Note
Staff may want to make a note on an action they took toward addressing a request, such as: making a phone call or leaving a note to the assigned staff member. In such cases, the private note should be used. These notes are logged within the request history however, no email is sent to the Customer (nor is there an option to send the note via CC or BCC).
External Note
The external note capability allows Staff to work with the necessary resources while still having the entire interaction logged within the request history. Customers do not receive email updates when an external note is used; only the specified recipients will receive the message when an external note is created. The external note options are the same as the public note options (CC/BCC options).
7.4. Request Note Hotkey Autocomplete
There are several autocomplete hotkeys that can be activated in the note editor. After a hotkey is entered in the editor, continue to type the search term desired to bring up the menu of matching options.
| Hotkey | Action |
| @ | Allows staff members to be tagged by name in a request note. Tagged staff members will receive a notification. |
| # | Inserts responses by title. |
| $ | Inserts placeholder variables. |
The video below covers how to use each of these hotkey combinations.
7.5. Request History
Every action completed on a request is logged within the request history. Actions can range from a note to the Customer to the logging of request detail changes. Logging all interactions enables any User, at any time, to become current on the happenings within a Customer request.
Users also have the option to filter history by: Full History, Only Notes, Public Notes, or Files.
Individual Entries: Up-Close
While the actions that create the entry may vary, the basic look and feel of all entries remains the same.
HelpSpot includes the following in every entry type:
- Time/Date Stamp of action
- Clear label of entry type (ie: Public/Private/External Note or Event Log)
- User name and photo, if available, for all User-generated actions
- Message recipients, when applicable
- Message, when applicable
- Description of request detail change, when applicable
The request history item menu provides access for the following:
- Quote a previous entry in a new note
- Change note status to public or private (excluding system-generated entries)
- Convert an individual entry into it's own request
- Generate a direct link to this entry. Handy for sending to another User for quick review.
Each note in a request history can be pinned using the "pin" icon. Pinning causes the request note to always appear at the top of the request history.
Across all entry types, images attachment are embedded within the request history for ease of viewing. For all other file types, there will be a link for downloading.
7.6. Request Details
The request details area contains the information necessary to manage the working of the request as well as the data to classify the request for reporting or automated processes.
Status
Users have the ability to assign a status to a request. A status assignment can reflect a milestone in the resolution process, including what led to the closure of the issue. For example, HelpSpot provides the following by default: active, problem solved, Customer found solution, Customer unreachable, and software bug. To close a request, Users must select a status type other than Active.
HelpSpot comes by default with a few status types to get Users started however; Administrators can customize the list of status types.
Category
On a very basic level, categories are used in HelpSpot to group-like requests together. This grouping can range from defining the nature of the inquiry to specifying the work group/department responsible for resolution. HelpSpot's flexibility allows organizations to best define the function that the category assignment serves.
It's important to keep in mind that beyond just a simple label, each category defines the types of meta-data collected for a request by tying request assignment, reporting tags, and custom fields directly to the category.
Appropriate category application, in conjunction with the meta-data collected, can provides help desks with a framework for workflow management.
Assigned To
Administrators must define the Users that have access to work requests within a specific category. Once this is done, Users will see on the request page a list of Staff to which a request can be assigned. This list will always contain:
- The default contact for the category,
- The Inbox as an assignment option. This means it will go to the Inbox and be available for anyone to take, and
- A count next to each Users name of how many requests are currently opened and assigned to them.
To select a Staff member, Users should use the dropdown to navigate available Staffers. Assignment is immediately applied as soon as the request is updated (via the Update Request or Update and Close buttons).
Assignment is the cornerstone of creating a request workflow. Once assignment is selected and submitted, the request will move to that User's My Queue and be flagged as unread for them to work.
Assignment can also be the basis for generating:
- Reports⎯monitor activity by User.
- Filtered Views⎯quickly navigate to requests based on assignment.
- Automation Rules⎯perform various actions based on request assignment.
Reporting Tags
Within each category an additional level of classification is available via the reporting tags. The selection of a value within the category drop-down will determine the reporting tags displayed.
Users can select as many reporting tags as applicable for the request by click the checkbox next to the tag. When the Update or Update and Close buttons are clicked, the tags will be applied to the request and logged within the request history.
At anytime reporting tags can be un-checked when no longer applicable.
Because HelpSpot ties reporting tags to the categories, when a category changes, any reporting tags selected under the previous category will no longer apply and new tags must be selected.
Reporting tags can be used to create:
- Reports⎯monitor requests by an additional level of classification.
- Filtered Views⎯quickly navigate to requests that contain specific reporting tags.
- Automation Rules⎯perform actions based on an additional level of classification within the request.
Custom Fields
Custom fields represent custom meta-data that can be collected for a request. There are 11 types of custom fields available to Administrators for creation. These data field types can be used in a various combinations to collect the information necessary for meeting specific business requirements.
In addition to showing custom fields on the request pages for Users, Administrators can also make selected fields available to Customers via the portal web form (note: not all are available in the portal). In these cases, a custom field that is populated by the Customer will be displayed to the User on the request page.
Custom field values are applied to the request as soon as the Update Request or Update and Close buttons are clicked. Custom field changes/updates are logged in the request history.
Uses for custom fields include:
- Reports⎯monitor requests by key indicators as defined by Administrators, not HelpSpot.
- Filtered Views⎯quickly navigate to requests that meet values specified in custom fields.
- Automation Rules⎯perform actions on requests based on organization-specific information.
Options
Within the header of the request details, there's an options menu that allows Users to:
- Set Reminders - Set a reminder specific to the request, using the reminders icon along the request details header. Reminders can include a note along with the inclusion of additional Staff. All reminders for the logged in User are in the user menu.
- Merge Requests - Combine one or more requests.
- View Access Key & Password - Customers must use the access to lookup a request on the portal. To access all their requests, at once, Customers must login using their email and password.
- Trash - Remove the request from the system; will no longer be included in filtered views or reporting.
- Print - Users can select to print a printer-friendly version of the request.
8. Responses
8.1. Responses
Responses are predefined messages, available to Users when updating requests and/or responding to forum posts.
Responses can be created with stylized text (bolding, bulleted lists, etc.) and contain placeholder information, such as assigned Staff members' email addresses or request IDs. Additionally, specific actions can be tied to the use of a response (ie: changing categories, status, or assignment). As with the use of the response itself, the associated actions can be a huge time saver for Staff.
The page is broken out into a complete list of all active responses (click to edit each). Below the list is the form to add a response. Users will be required to define a name, location, and permission access for the response.
Formatting
Placeholders
{{ $requestid }} - Request ID
{{ $accesskey }} - Access Key
{{ $replyabove }} - "Reply Above" Text
{{ $portal_email }} - Portal Login Email
{{ $portal_password }} - Portal Login Password
{{ $customerfirst }} - Customer first name
{{ $customerlast }} - Customer last name
{{ $customerid }} - Customer ID
{{ $customeremail }} - Customer email
{{ $customerphone }} - Customer phone
{{ $status }} - Status
{{ $category }} - Category
{{ $urgent }} - Urgent
{{ $open_closed }} - Open/Closed
{{ $date_opened }} - Date Opened
{{ $date_now }} - Date Now (current date/time)
{{ $assigned_first }} - Assigned staff member: first name
{{ $assigned_last }} - Assigned staff member: last name
{{ $assigned_email }} - Assigned staff member: email
{{ $assigned_phone }} - Assigned staff member: phone
{{ $logged_in_first }} - Logged in staff member: first name
{{ $logged_in_last }} - Logged in staff member: last name
{{ $logged_in_email }} - Logged in staff member: email
{{ $logged_in_phone }} - Logged in staff member: phone
{{ $subject }} - Original mail subject line
{{ $initialrequest }} - Initial Request Note
{{ $orgname }} - Organization Name
{{ $helpdeskurl }} - Help Desk URL
{{ $requestformurl }} - Request Form URL
{{ $requestcheckurl }} - Request Check URL
{{ $knowledgebookurl }} - Knowledge Book URL
Request Actions
Users can expand the power of the response by defining specific actions to be taken on the request when responses are applied. Actions can range from updating a category or status to adding a private note. Any actions taken as a result of a request, will be logged within the request history.
Reoccurring Requests
Responses can be optionally turned into reoccurring requests that create new requests at a specified interval.
8.2. Response Permissions
Overview
HelpSpot Responses are predefined replies or templates that can be used to quickly address common inquiries or issues. This documentation covers the permissions and capabilities associated with editing and ownership of these responses.
Editing Permissions
Admins
- All Admins Can Edit All Responses: Administrators have the privilege to edit any response, regardless of who originally created or owns it.
Owners
- Editing Own Responses: Response owners, i.e., the users who originally created a particular response or has been assigned ownership, have the ability to edit that specific response. This allows them to make updates or corrections as needed.
Usable By
- Responses can be shared using the Usable By field. Responses that are shared with groups of users will be usable by that group. However only the Owner and Admins will be able to edit the response.
Ownership and Transfer
The owner of a response is the user who originally created it or the user to whom ownership has been transferred. There are two sets of users who can transfer ownership, the Current Owner or an Admin.
Transferring Ownership
-
By the Current Owner: The current owner of a response can transfer its ownership to another user. This might be done if the original owner is leaving a team or believes another user is better suited to maintain the response.
-
By an Admin: Administrators also have the capability to transfer the ownership of any response to another user. This can be useful in scenarios where the original owner is no longer available or if there's a restructuring of responsibilities.
Steps to Transfer Ownership
- Click on "Responses" from the main menu.
- Find and select the response you wish to edit.
- Scroll to the "Response Owner" field.
- Choose the new owner from the dropdown list.
- Click "Save" to confirm the changes.
9. HelpSpot AI
9.1. AI Action Prompt Usage
HelpSpot AI action prompts allow you to perform AI tasks on text in the request not editor and in the knowledge book editor. The action prompts that are available in your system are determined by your HelpSpot Administrator.
Action prompts can be accessed in two different ways.
- Typing an exclamation point (!) immediately followed by part of the name of the action prompt will allow you to autocomplete and trigger the action:
- You can also browse the available action prompts from the top of the WYSIWYG editor under the HelpSpot AI menu.
AI action prompts can be applied to all of the text in the editor or to a selection. If you want to apply an AI action prompt to a selection of text first select the text and then select the prompt from the menu. The {{ input.text }} placeholder will only include the text selection in this case.
9.2. AI Request History Translation
When HelpSpot AI is enabled. Staff members can translate request history items using HelpSpot AI. The translation is temporary and the original text is always preserved in the database. To translate a request history item select the request history menu and then choose "Translate" from the menu.
The translation will be performed from any language to the language selected as the Translation Language in Admin > HelpSpot AI > AI Settings.
10. Knowledge Books
10.1. Public vs. Private
Knowledge books allow an organization to create documentation for their products/services. Books are organized with chapters and pages, providing a familiar structure for ease of navigation.
Throughout this section reference will be made to public and private knowledge books, the differences are:
- Public. Intended for Customers. These knowledge books are available via the portal and through the KB area within HelpSpot (by Staff only).
- Private. Intended for Staff only. These knowledge books are accessible only via the KB area within HelpSpot.
10.2. Adding/Editing Books
Book Creation
Within the Knowledge area, books can be created via the Add a Book button.
During book creation, specify the book-level properties such as name, book editors and book type (public/private).
As soon as a public knowledge book is added it will be live on the portal. To prevent Customers from seeing partial books, select Yes to making your books private until you're ready to have them go live.
Ordering Books
Using the Books Order button, Users will be brought to a page to sort either the public or private books.
Editing & Deleting Books
All books (public and private) are listed on the left navigation. To edit any one of those books, click the title and use the edit book button within the book table of contents screen. The form to modify is the same as the one used to create the books. Keep in mind that when a book is deleted, all content within the book is deleted as well and cannot be recovered. When it's gone, it's gone!
10.3. Adding/Editing Chapters
Adding Chapters
Within the book table of contents page (accessible by clicking the left navigation), Users should use the Add Chapter button.
Chapters default to being visible (not hidden). Hiding chapters is useful when adding content to an existing, live book.
Chapters can be designated as an appendix, meaning they will appear at the end of the book without a chapter number.
Editing Chapters
Next to the chapter name on the book table of contents page is the edit chapter button. It is through this area the parameters of the chapter can be modified or a chapter can be deleted. Keep in mind that when a chapter is deleted it can not be recovered. When it's gone, it's gone!
10.4. Adding/Editing Pages
Adding Pages
Again, from the book table of contents page, Users should use the Add Page button located next to each chapter name to add a page within that chapter.
Adding pages is a two-step process. The first step requires naming and sorting order be selected. During the second step page content is created. Pages are defaulted to being hidden, viewable only to editors, for the purposes of creation. When you're ready to go live simply flip Hidden to No.
Editors can also link related pages, flag a page as highlighted or add an attachment file to complete the content of the page.
Formatting Pages
The built in visual editor, allows Editors to stylize and format the content without the hassle of hand coding the necessary web mark-up. Type the desired content into the text box, highlight, and select the desired action from the tool bar. Images can be drag and drop uploaded or copied and pasted into the editor.
Knowledge Tags
Each page can have any number of knowledge tags associated with the page content. For more on how to set knowledge tags and how they work see the knowledge tag page, linked under related pages.
Editing & Deleting Pages
Clicking the chapter title, within the books table of contents, to get to the page content. The page editor is accessed through the edit page button. From here, pages content and properties can be edited. When pages are deleted all content will be lost and cannot be recovered. When it's gone, it's gone!
10.5. Knowledge Tags
Knowledge Tags allow Users to create a cross-resource base of knowledge. The advantage over traditional search is it's a much quicker, accurate way for readers to find specific content across knowledge book pages and forums.
Applying Tags
Knowledge Tags can be applied to by Users to any knowledge book page or forum topic; during or subsequent to creation. Users should take care to include every/all relevant tags as this will maximize the pertinent results returned.
Tagging consistence across content is critical. As Users type to add a tag, HelpSpot will show existing matching tags. You can opt to select the tag, if applicable, or continue to type the full tag.
Tags in the Portal
Your portal users can access Knowledge Tags in alpha order at the bottom of the homepage. Readers can click any tag to get a complete list of Knowledge Book pages with that tag. Notice the variation in size. The relative size of the tag name corresponds to the number of times it occurs within the content.
When Readers search within the portal, there's a section that will return the exact match Knowledge Tag (if such exists).
Advanced Search and Tags
Users can search within Knowledge Tags using the Advanced Search in HelpSpot. Tags can be search individual or combined for the desired results set.
11. Reports
11.1. Todayboard
Completely redesigned, HelpSpot's Reports area is a robust, graphical-rich way of monitoring your help desk.
Todayboard
The landing page for the Reports area is the Todayboard, which is 6 distinct reports to provide a high-level look at the activity of the help desk.
Today's Request
Broken down by each hour of the day, this report shows requests opened today (24 hour period) and also compares that to activity of that 1 week ago. Allowing Users to see request activity today, throughout the day, relative to the same day last week.
Number of Replies to Close
As the title would indicate, this report show how many public notes were submitted (per request) by Staff prior to closing.
First Response Speed (Biz hours)
The average and median for how long (in hours) until requests had a public note added by Staff. This is calculated within business hours (default is 8-5, local time).
Top Workloads Currently
Staff (3) with the most number of requests currently open.
Top Categories
Shows the top five categories to which requests are being assigned.
Interactions
An hourly look at request types, broken out by type: public by Staff, private by Staff, and Customer.
11.2. Canned Reports
HelpSpot includes built-in reports that allow Users to monitor various aspects of activity on the help desk. Reports are broken out in to 3 groups: Requests Over Time, Analysis, Portal, and Time Tracker.
Report Characteristics
While reports differ in the data pulled, all reports have the following characteristics in common:
- For quick use, every report has a graphical representation of the results set.
- Hovering over any data point on a graph will provide the specifics (ie: date, time, or count).
- All reports provide the data set in list format that can be quickly accessed through the Data tab. It is from here you can drill down to see individual requests, as desired.
- When applicable, the median and average values are provided.
- Unless otherwise stated, the default time period is two weeks.
- Any modified report can be saved for future use.
- Reports can be exported in .csv format for manipulation outside of HelpSpot.
Modification Available for All Reports
All reports allow for the following parameters to be set:
- Time/date ranges
- Filtering. Any report can have filtering parameters added to refine the results returned. Filtering conditions are discussed within each report where relevant.
Requests Over Time
Perhaps the best overall look at the activity of the help desk, this report is broken out within the Reports navigation.
Requests over Time shows a count of requests (those opened) each day over the course of a 2 week period.
Modifications available for this report:
- group results by: time period, aggregate time period (ie: day of week/month of year), request detail item, or custom field.
Comparison Matrix
The comparison matrix report provides two axis of data compared in a heat mapped matrix. The matrix report will allow you to quick spot trends and analyze segmented help desk data ways that were not previously possible.
Modifications available for this report:
- Both axis can be selected from a list of available fields.
Productivity Overview
The productivity report allows the user to view first response and closing speeds in time layers.
Modifications available for this report:
- group results by date
- calculate based on business hours or 24 hour period
- group results by date
- calculate based on business hours or 24 hour period
First Response Speed
Shows the number of hours taken for Staff to update requests with the first public note.
Modifications available for this report:
- group results by date
- calculate based on business hours or 24 hour period
- show speed rates by hours or minutes
First Assign Speed
Time it took to be assigned to Staff from first entering the system. This report is most applicable for those NOT using automation or mail rules for auto-assignment.
Modifications available for this report:
- group results by date
- calculate based on business hours or 24 hour period
- show speed rates by hours or minutes
Replies by Count
Number of public updates done by Staff. Commonly used to see how many Staff updates were necessary to close a request. When using for this purpose, be sure the Open/Closed filter is set to Closed (defaults to all).
Modifications available for this report:
- group by count (prevents excessive spread in x-axis)
Interactions over Time
Count of notes, broken out by type, based on note creation date.
Modifications available for this report:
- group results by date
- group results by author (HelpSpot User & Customer)
Resolution Speed
Time taken (in hours) for a request to be closed.
Modifications available for this report:
- group results by date/month/year
- calculate based on business hours or 24 hour period
- based on date open or closed
Searches/Few Results
List of search terms used by Customers, which yielded the fewest results. Note, this report does not have an accompanying graph.
Aggregate Searches
List of search terms using in Customer portal. Those used most frequently are listed first.
Response Usage
Count of most used responses. List includes response title (link to response), response creator, and usage count. Users can use filtering to find the most used responses with a specific category or status type.
Modifications available for this report:
- specify Staffer or all Users
Customer Activity
Count of those Customers with the most requests in the system (defaults to include both open & closed).
Modifications available for this report:
- select unique identifier (email, name, or customer ID)
- limit results returned
Time Tracker: Time Events
A list of all time events logged by Staff. The request ID listed in each event can be click to view the Request.
Modifications available for this report:
- group results by date/month/year
- group by individual Staff
11.3. Editing and Saving Reports
As discussed in previous pages, Users can further refine the results set (ie: modify the parameters) in a number of ways.
- Adjust time frame
- Group results (discussed in specific reports on previous page)
- Use of Filter conditions
Using Report Filters
There are numerous filter conditions that can be applied only, or in conjunction with other conditions, to define the exact information needed. The filter conditions available in Reports are the same as those used within the Filter creation process.
Saving Reports
Once you've created a report that is tailored to your needs, it can be saved for future use. Saved reports can be organized into folders and shared with other staff members.
11.4. Scheduled Reports
Scheduling Reports
Reports can be scheduled under the Save + Email tab of the report interface.
A scheduled report will be emailed to selected individuals on a given time period. When a report schedule is setup the time period for the report will be adjusted each time the report is run.
11.5. Sample Reports
Below represents a few of the report modification that can be made to find specific information; those areas most commonly monitored by help desk administrators/managers. As mentioned previously, any report can be saved in the My Reports folder for future use.
Grouping by Category, Assigned User or Custom Field
Base report. Request Over Time.
Description. Users can quickly see requests over time based on category, assignment or any custom field by using the Grouping drop down, as shown below.
Implication. Insight into any of these areas will allow managers to make adjustments such as: increased portal documentation on a particular topic (addressing high categories), use of auto-assigment to better balance workload, or coordination with other departments.
Filtering by Customer
Base report. Request Over Time.
Description. Using the filtering conditions, Users can see requests submitted by a particular customer or customers meeting specific criteria within the Customer Information fields (ie: email domain or customer ID). Different from creating a Filter, this report will give you an aggregate snapshot over a defined period of time. Note: for this example, Customer email domain was used, in addition the results are being grouped by status and the time frame has been expanded.
Implication. Managers can use this to monitor service agreements or other contractual commitments.
How Many Replies to Close
Base report. Replies by Count.
Description. Find the aggregate of how many public notes occurred prior to an issue being closed. This type of report can be used as a gauge to determine how much work is required to resolve issues. Note: the filter condition of Open/Closed was set to Closed for this report.
Implication. Higher numbers within a particular category/reporting tag area or by select individuals could indicate a need for increased training or revision/creation of prepared responses.
12. Customer Portal
12.1. Homepage
The portal is the Customer-facing site for HelpSpot. It's designed to enable self-service and provide Customers with a centralize location for all support-related information/activities. From the portal Customers can:
- Use the web form to submit an inquiry,
- Check the status of an inquiry (or login to check status of multiple inquiries),
- Search and browse knowledge books to find solutions.
While this manual uses one of the available default portal styles, it's important to note that HelpSpot's portal is fully customized; allowing consistency with the look of any company's website/intranet.
HelpSpot can support multiple (secondary) portals. This is used when separate customer facing support areas are needed. Configuration is done through the Administration area of the installation.
Given portal functionality is consistent across primary and secondary portals, the balance of this chapter will focus on the use of one, the primary, portal only.
Lay of the Land
When Customers enter the portal they'll see three distinct areas on the homepage
- Header and Search. Allows Customers to search forums or knowledge books.
- The Left Navigation. Links for submitting/checking/updating requests as well as links to any knowledge books (if public).
- Center of page. Grouped lists of links to items that were highlighted by editors (knowledge books), flagged by readers as most helpful (knowledge books), and the knowledge tag cloud.
12.2. Knowledge Books and Forums
Knowledge Books
Public books are highlighted in four areas within the portal:
- The portal homepage lists the knowledge book pages editors highlighted during the creation process.
- On the portal homepage, those pages voted most helpful.
- The left navigation will list all public knowledge books.
- Searching can be done within knowledge books.
Once a knowledge book title has been clicked, readers are brought to the table of contents, which includes all live chapters/pages with editor-specified pages highlighted for the reader, if applicable.
Clicking on a page title will bring readers directly to the page content. Readers can vote on the helpfulness of a page. An aggregation of the most helpful pages from all public books is listed on the homepage.
12.3. Submitting and Checking Requests
Submitting a Request: the Request Form
Using the link on the left navigation, Users can submit a request.
By default HelpSpot requests a simple problem description. Administrators can change the request description boxes to a three areas: what I did, what I expected to happen, and what actually happened.
Some installations may create custom fields and/or categories that they wish to make public to enable request workflow or capture additional information directly from the Customer.
To help reduce SPAM, captcha can be turned on by administrators.
Check and Update Requests
Customers can use the Check on a Request link, within the left navigation, to check on and update requests. Customers must provide the request access key, which is provided by default in the emails Customers receive, to see a specific request.
For the quickest and easiest access to all their requests, Customers should login into the portal using their email address (one provided when submitting requests) and password. If the customer has never submitted a request they can create a new account.
Passwords can be retrieved via the forgot password link. Once logged in, Customers will see a list of all requests they have (opened and closed) as well as the option to change their password for future login.
Just below all public update entries and the initial request, Customers will find an open text field where additional updates.
12.4. Section 508
Section 508
Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act (29 U.S.C. § 794d), as amended by the Workforce Investment Act of 1998 (P.L. 105-220) requires federal agencies to develop, procure, maintain and use information and communications technology (ICT) that is accessible to people with disabilities - regardless of whether or not they work for the federal government. The US Access Board established the Section 508 standards that implement the law and provides the requirements for accessibility. You can read more about it from the official section508.gov website.
The public-facing portal of HelpSpot is fully 508 compliant, we use a tool called WAVE that is developed by WebAIM. This tool creates a report showing any errors with the code markup, any contrast errors, and more. You can see the results from running this on the portal home page as we have below:
The HelpSpot portal is also fully customizable and you can modify and change every part of it to not only match your brand but also address any regulations you need to meet.
The customer portal is the area of HelpSpot that your customers use to submit requests and view your documentation. Being fully 508 compliant ensure that all your customers are able to reliable access the portal.
HelpSpot Agent Interface
The HelpSpot agent interface is the 'app' part of HelpSpot where your support agents can manage incoming requests. This area is much more technically complicated and is only partially 508 compliant at this time, though it's an area we continue to improve each release.
This part of HelpSpot is only used by agents of the system, end customers never access this area.
Appendix: Feature In-Depths
1. Filters in Use: Working Example
Filters are a way to view create custom views of the requests. By default, HelpSpot ships with global 'All Open' and 'Recently Closed' filters. However, an infinitely combination of conditions can be combined to create a filter that meets your excact business need.
Here are 3 real world examples of Filters in use. Execution of these filters can vary, with additional conditions being layered on to meet the business need, but the following shown here is intended to give Users an idea of how each would be created.
1. Monitoring Contractual Commitments
Business Need: Support desk has a contractually agreement with Customer group (internal or external) to always respond to equipment issues within 24 hours of Customer updates.
Creation: Filter must be created to see those requests that haven't been updated within 24 hours, that has been assigned to Category: Equipment/Reporting Tag: Issues.
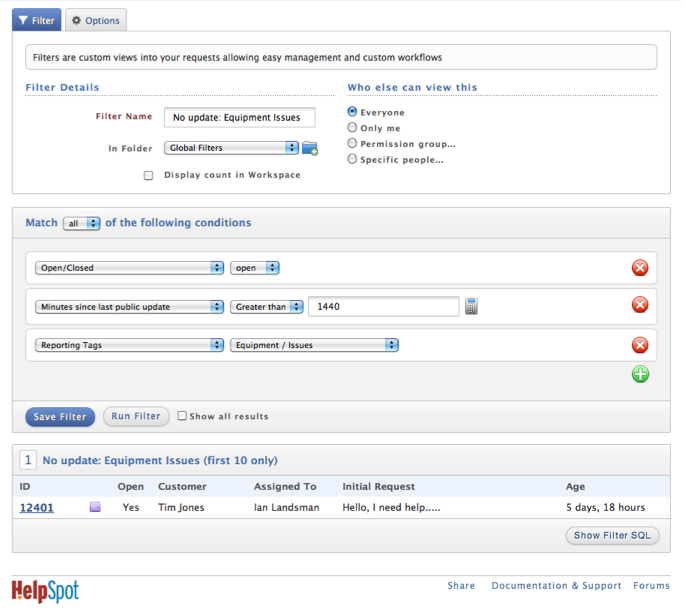
2. Creating Custom Inbox
Business Need: Create an Inbox for only those Staff working Account inquiries. Allows those Users to focus on working only those requests within their area of expertise.
Creation: Filter must be created to see those requests assigned to the Account Inquires category.
Unique to this filter is:
- selection of Staff that can access the filter
- addition of Take It button (not shown below but found under the Options tab).
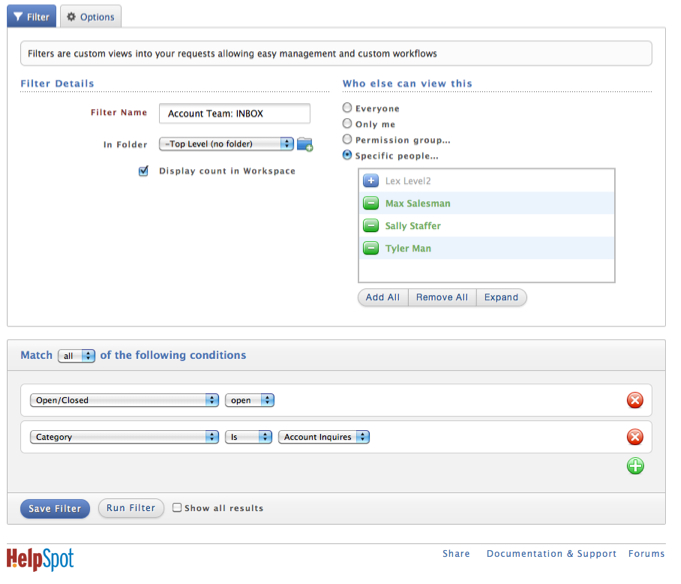
3. Monitor Activity of Selected Staff (Training)
Business Need: Monitor activity of selected Staff. Effective in providing timely feedback during training periods.
Creation: Filter must be created to see those requests opened Today, assigned to Staffer X, and are either currently Open or Closed.
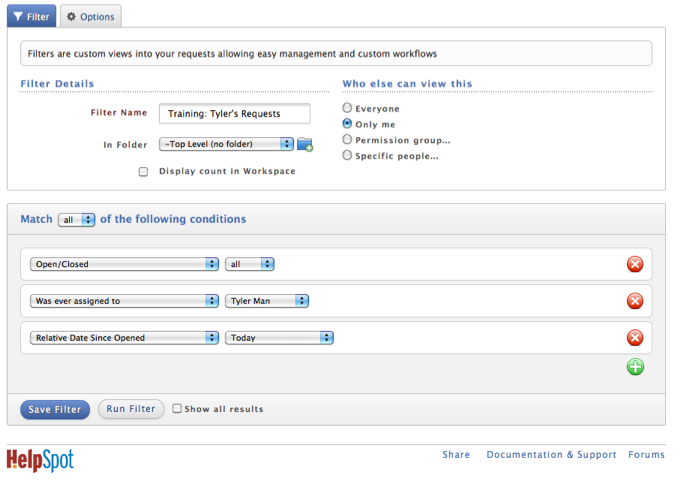
2. User Preferences
Once an account is created, each User has the ability to set/edit preferences by click their name in the top right corner of the screen.
The preferences page covers everything from password changes to signature creation and allows Users to personalize their HelpSpot experience.
Make sure you hit Save at the bottom of the page to ensure all changes are applied.
Email and Password
The name, email, and password are displayed, at the top of the preference page, to the User as entered by the administrator during account creation. Users have the ability to update this information.
The email address listed here for Users is the default address HelpSpot uses for sending notifications.
Black Box Username
This is only required for Users in installations that are running alternative authentication with an external source (such as Active Directory).
Photo/Icon
Users can select from an emoji library or opt to upload their own photo. The selected photo is used as part of the request history when the User creates an update, serving as a quick means to identify individual Users.
Users should resize images to 32x32 (pixels) prior to uploading to achieve the best results.
API Key Creation
Users can create an manage their api keys for interacting with other applications.
Communication
The communication area defines alternative contact information, out of office manager, as well as signatures for outgoing messages.
Alternative Contact Information
HelpSpot provides Users with a means for providing an alternative email, phone number, and SMS number. Options in the notification area allow Users to configure when messages/updates are sent via these alternative channels.
Out of Office Manager
If a User is going to be out of the office for an extended period of time, such as vacation or medical leave, all requests that would have been assigned to them can be assigned to an alternative User.
All Users are defaulted to being available. However, by using the drop-down Users can change their status and select whom their requests should go.
A visual indicator of out of office status appears in the assignment drop-down on the request page.
Creating a Signature
Similar to any mail client, Users can create a signature block that is appended to every outgoing message/update (public and external notes).
HelpSpot offers both a text and HTML signature format to account for varying system configurations. As such, it is recommended that Users complete both text and HTML to ensure the signature is included.
When creating the HTML version of the signature, Users must use formatted text mark-up.
There's a third tab within the signature creation area for creating a mobile-specific signature. This signature will be used only when a User creates a note using HelpSpot mobile. Often a varying signature is used to inform the reader the note was created on a mobile device.
Notification
The notification area allows Users to configure where and under what conditions they receive a notification. The list below outlines each of the notifications options.
- Send notification via email. Checked by default, so any system notification and request updates will generate an email.
- Alternative email notification. Unchecked by default, this option sends all notifications to the alternative email address.
- SMS notification options. HelpSpot allows Users to send all notification (that would typically go to an email account) to an SMS enabled device. Users can opt to select to send all notifications or only urgent ones. All SMS options are uncheck by default.
- Notification for unassigned new requests. User can opt to receive a notification for every unassigned request that enters HelpSpot. The notification method will follow the channel specified within the options described above. This is unchecked by default.
General Preferences
These general preferences help Users personalize their experience by defining specific aspects of the look and feel to match their personal work style.
- Default to public note. Selecting this will default the note type to public each time the User enters the request page.
- Disable WYSIWYG in the knowledge books. For Users that prefer to hand code HMTL they can opt to disable the visual editor (aka: WYSIWYG editor) for knowledge book creation.
- Do not embed images in request history. Selecting this option will treat images as other attachments and create a link at the bottom of the request history entry containing the image. By default, this is not enabled and all images are embedded within the request history entry.
- Return to request after closing. By default, when a User closes a request HelpSpot will return the User to the filtered view they were in prior to entering a request. Selecting this option will bring Users to a request summary page once a request is closed. Enabling this option will give Users an opportunity to double-check a request after closing but before moving to the next request.
- Show Getting Started Menu in Workspace. By default, HelpSpot will show all Administrators the Getting Started menu as a quick reference. This can be turned off, or on for other permission levels, simply by checking the box.
- Number of request history entries shown by default. Users can enter the desired number of request notes seen within the request history. HelpSpot defaults to showing 10 request history entries.
Regardless of the number set in the preference, Users can see all request history entries simply by clicking the Show All link at the bottom of the request history list on the request page.
- Default Request History View. Users can specify if they wish to see Full Histories or Only Notes for every request they view.
- HTML editor for HTML notes. For systems with HTML notes enabled (system default), Users can opt to create HTML notes via the visual editor, formatted text, or use the system default (which could be either method; system default is the visual editor). Use of either the visual editor or formatted text will result in an HTML email being generated. HelpSpot defaults Users to the system default: the note creation method as defined by the Administrator.
3. Merging Requests
The request merging feature forces the request history of one request into another. This is often used when multiple requests are created for the same Customer regarding the same inquiry.
Merging can be done from the:
- request grid view, via the quick action buttons, or
- within the request page, from the Merge link within the options menu.
Once the merge is complete, the User will be brought to the request page for the receiving request. The individual request histories of the merged request are inserted in chronological order within the receiving request. All merged histories are clearly identified, allowing you to retain an accurate account of all interactions.
Any responses to the original request are automatically routed to the newly created, merged, request.
Note: It is not possible to 'unmerge' once your requests have been merged together, so make sure you're certain you want to merge!
4. Batch Response/Edit
HelpSpot gives Users that ability to batch response/update requests. Meaning, from in the request grid view (Workspace) Users can select a group of requests and initiate a response to be sent or an update to be made in the request details without entering the request page for each, individually.
Batch responding is understood through a real world example: Within a 20-minute period a support desk receives dozens of requests about connectivity issues that is determined to stem from a server outage. Using Batch Response/Edit, Users can send a message to all applicable requests explaining the situation while also updating the status, category/assignment, or reporting tags.
For later follow-up, such as sending sending status update notification, Users can opt to have a link to the results added as a filtered view on the left navigation.
5. Time Tracker
For installations with this enabled, the time tracker will be across the top of the request page. It allows each User to log the time spent on a request. Time tracking is primarily used by organizations for billing/customer contract purposes.
Time can be entered manually or through the use of the stop-clock. When manually entering time, decimal or standard time format (for example: 2.5 or 2:30) is accepted in the hours/minutes box. When using the stop-clock, click the arrow when work starts on the request and click it again when work is complete. The time lapsed will be logged for the entry. A field is provided to provide a brief description of the work completed during that logged session.
HelpSpot includes a Billable checkbox, allowing Users to flag time which would be billable for later reporting.
Users can also use the options menu to log time for another User, if necessary, as shown below. If time is logged without selecting from the options area, the time will be attributed to the logged-in User.
Once Users click the Log Time button the time will be listed as part of the aggregate time spent on the request.
To report time logged across all requests, use the Reports area.
6. HelpSpot Mobile App
HelpSpot Mobile is available on both the Google PlayTM and the iOS App Store. The Helpspot mobile app provides a streamlined mobile user interface for interacting with the HelpSpot application. The HelpSpot app will work on both self-hosted and HelpSpot Cloud instances.
Getting Started With The Mobile App
Since the mobile app connects to your instance of helpspot you will need the URL of your helpspot site the first time you login to the mobile app.
- Open the mobile app
- Enter the URL to your helpspot instance. For example: https://helpspot.yourdomain.com
- Enter your username and password
If you encounter issues logging in. Visit our troubleshooting guide.
Android, Google Play and the Google Play logo are trademarks of Google Inc.
Apple and the Apple logo are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
7. Need Help?!
Below are the support-related resources available for HelpSpot.
- HelpSpot's Knowledge Books and Forums (https://support.helpspot.com/) provide more specific information around setting up and optimizing HelpSpot.
- Submit a request for assistance via the request submission form (https://support.helpspot.com/index.php?pg=request).
- Email questions/inquiries to customer.service@userscape.com.
- The HelpSpot User Forum is available at https://discuss.helpspot.com.